How are Lab Grown Gemstones made?
CZOCHRALSKI PROCESS
Melting
The process begins by melting the starting material, often a mixture of high-purity aluminum oxide and a chromium-containing compound, in a high-temperature crucible, typically crafted from materials like quartz or graphite. The temperature is meticulously controlled to achieve a molten state without degradation.
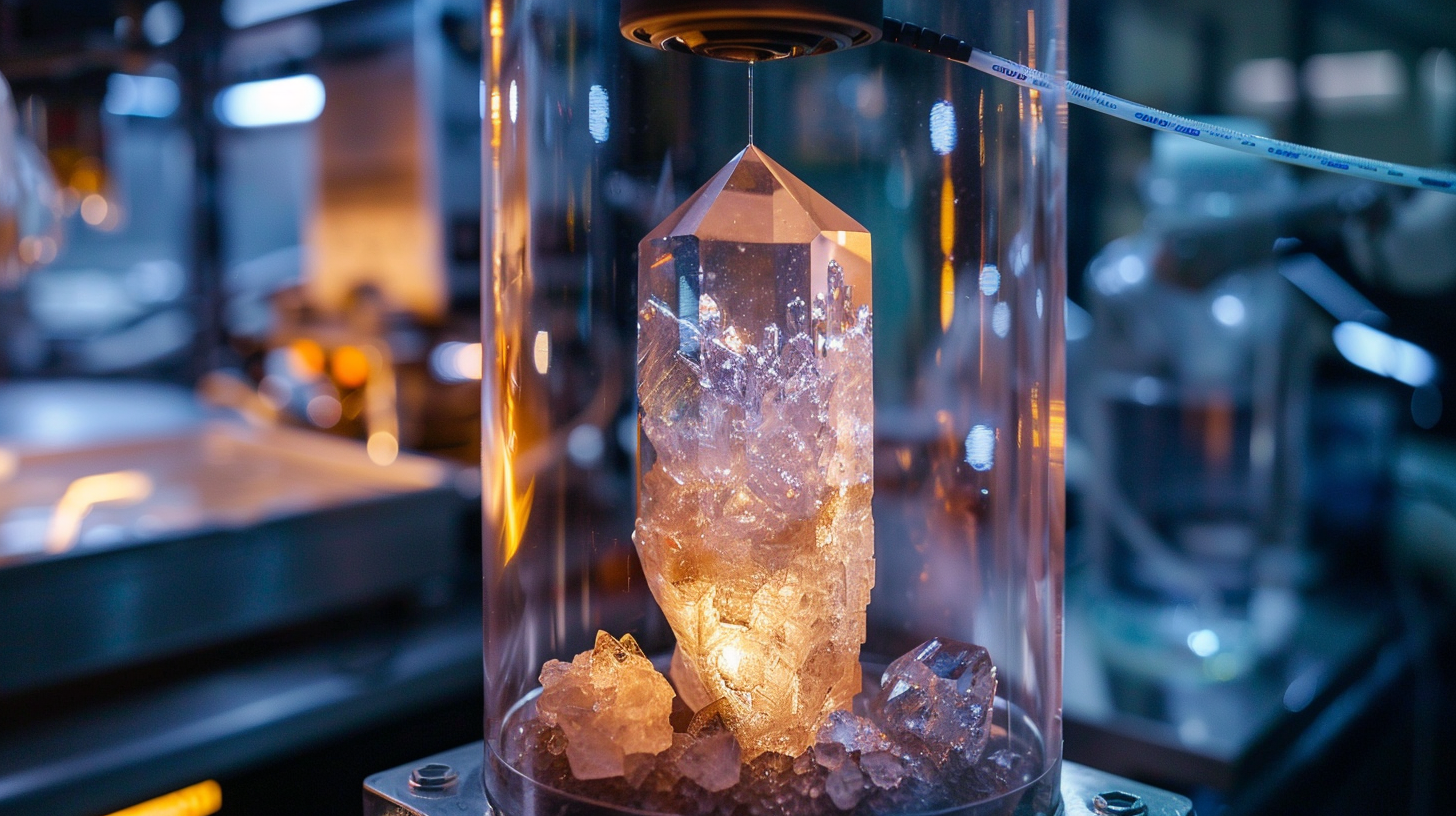

Crystal Seeding
A single crystal seed, typically composed of low quality Corundum (Ruby or Sapphire), is cautiously lowered into the molten material. This seed crystal serves as a nucleus for the growth of a larger single crystal, with its orientation dictating the orientation of the resulting Corundum crystal.
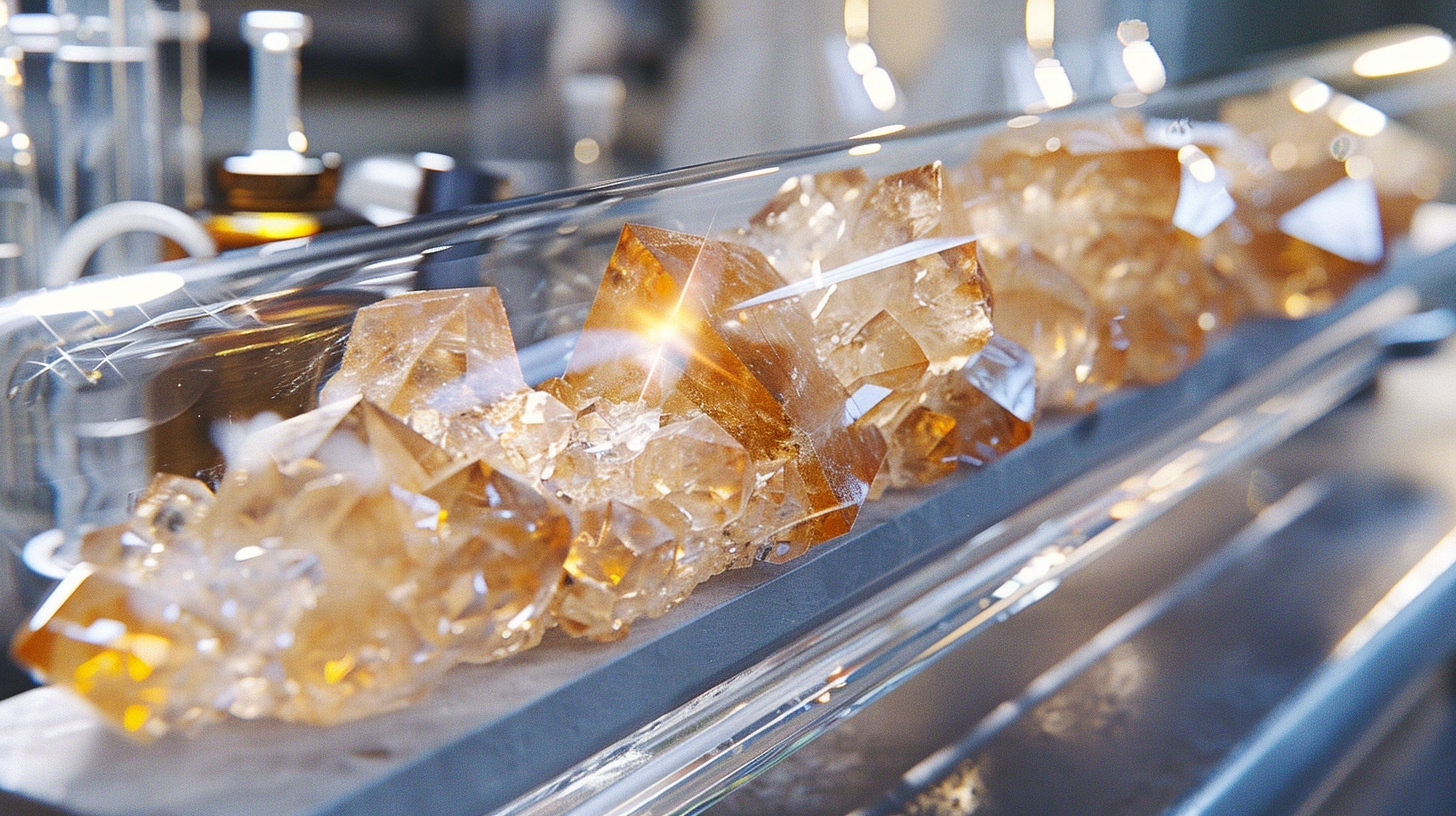

Crystal Growth
Once the seed crystal is in position, the crucible is methodically rotated and lifted upwards at a controlled pace. As the crucible rotates and the seed crystal is gradually withdrawn, material from the molten pool adheres to the seed crystal's surface, forming a single crystal structure. The rotational speed and pulling rate are crucial factors in governing the size, shape, and quality of the resultant ruby crystal.
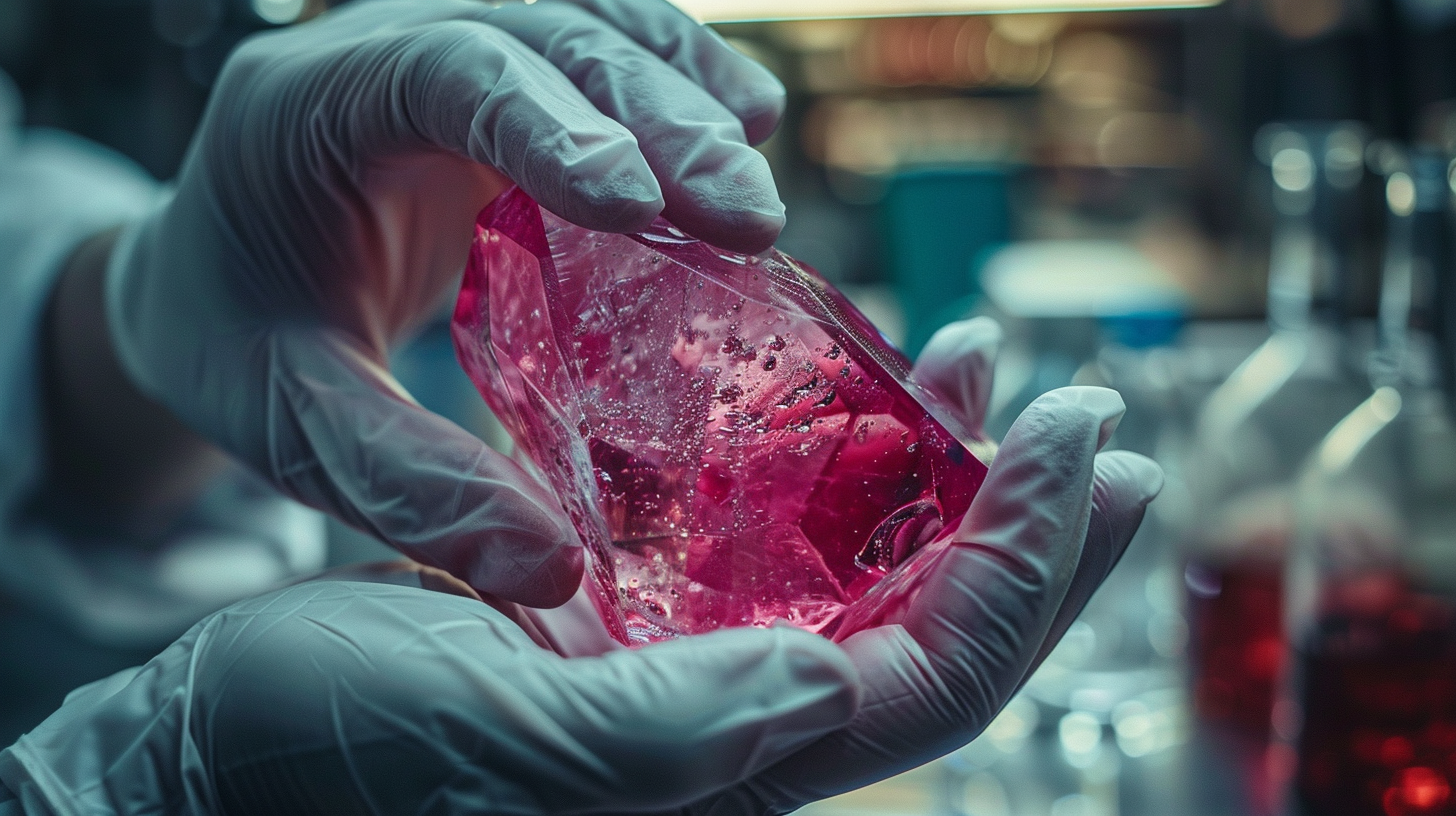
Cooling and Solidification
As the ruby crystal expands, it undergoes gradual cooling to solidify the material into a single crystal structure. This cooling process is typically managed to avert thermal shock and ensure uniform crystal growth. Upon reaching the desired size, the ruby crystal is delicately extracted from the crucible and undergoes further processing steps, including cutting, polishing, and treatment, to enhance its color and clarity for various applications.
